 |
ALKYLATION
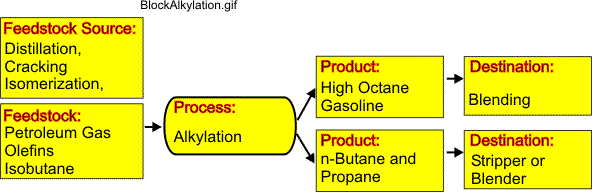
The figure provided here illustrates the block diagram for an alkylation process.
Alkylation combines low-molecular-weight olefins (primarily a mixture of propylene and butylene) with isobutene in the presence of a catalyst, either sulfuric acid or hydrofluoric acid. The product is called alkylate and is composed of a mixture of high-octane hydrocarbons.
Alkylate is a premium blending stock because it has exceptional antiknock properties and is clean burning. The octane number of the alkylate depends mainly upon the kind of olefins used and upon operating conditions.