 |
ISOMERIZATION
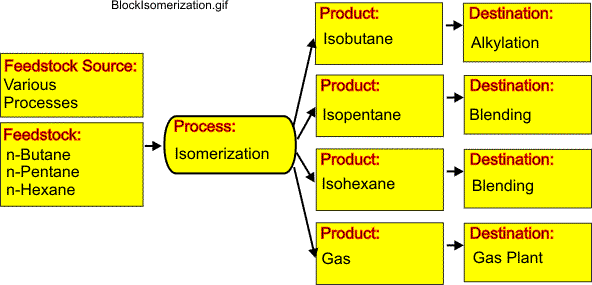
The figure provided here illustrates the block diagram for an isomerization process.
Before we go any further, let’s have a quick discussion about “normal” and “iso” types of hydrocarbons.
Some hydrocarbons, such as butane occur in two forms: normal butane (n-butane), or isobutane (i-butane). Both of these chemicals have the same number of hydrogen and carbon atoms, but the molecular structure is different. Due to the difference in the molecular structure, chemical and physical properties of the two chemicals are different. For gasoline production i-butane is more desirable than n-butane.