 |
CRUDE OIL DISTILLATION (FRACTIONATION)
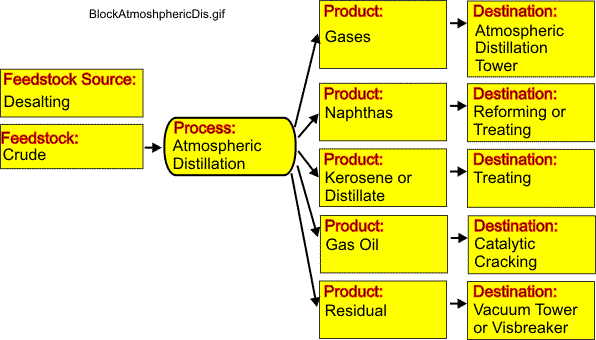
The figure provided here illustrates the block diagram for the operation of an atmospheric distillation system.
The first step in the refining process is the separation of crude oil into various fractions or straight-run cuts by distillation in atmospheric and vacuum towers. The main fractions or "cuts" obtained have specific boiling-point ranges and can be classified in order of decreasing volatility into gases, light distillates, middle distillates, gas oils, and residuum.
Note the word “distillate” used here, we’ll be using it many times later on. The term “light distillate” indicates a hydrocarbon which has a lower boiling point in comparison to a “middle distillate” or a “heavy distillate.” The common thread among all these hydrocarbons is that they are generated by a distillation process - hence all of the three are distillates.