 |
Radiant and Convection Section Tubes
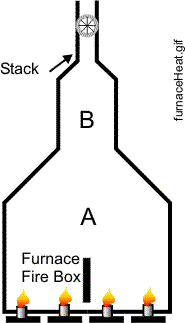
In a furnace, heat is absorbed by liquid-carrying tubes in two distinct regions: Radiant and Convection Sections.
Most of the radiant heat is limited to the firebox. To absorb this radiant heat, the firebox is lined with liquid-carrying tubes. These tubes are known as radiant tubes. The radiant tubes operate at a high temperature, therefore they are constructed with high-alloy steels. In most furnaces, 70% of the total absorbed heat is absorbed in the radiant section. In the figure, region A is the main radiant heat region.
Availability of the radiant heat is based on the “line-of-sight” principle. Therefore, radiant heat is absent in all regions of the furnace which are not directly in line-of-sight of flames or hot refractory bricks surrounding the firebox.
As flue gases flow out of the firebox, they carry along an enormous amount of heat. To absorb this heat, some regions in the path of the flue gas are also lined with tubes. These tubes are referred to as the “convection tubes”. In most furnaces, about 30 to 40% of the total absorbed heat is absorbed in the convective regions of the furnace. In the figure, region B is the main convection region.