 |
Turns Ratio
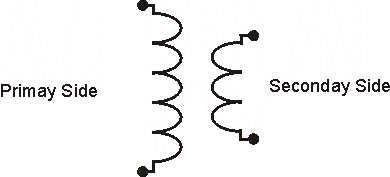
In the figure shown here, we see a schematic sketch for two coils of a transformer. The coil, which supplies power to a transformer, is referred to as the Primary Coil. The coil in which voltage is induced by the Primary Coil is known as the Secondary Coil. Now the next question is how much voltage is induced in the secondary coil? That depends upon the ratio of the coil-turns between the two coils.
Example 1
Given data:
Voltage of primary coil = 220 volts
Primary coil turns: 500
Secondary coil turns: 1000
Find the voltage induced in the secondary coil.
Since the secondary coil turns are twice as many as those in the primary coil, the induced voltage will be twice as much. Therefore, the induced voltage will be equal to 440 volts.
We refer to such transformers as “Step-Up Transformers”.
Example 2
Given data:
Voltage of primary coil = 220 volts
Primary coil turns: 500
Secondary coil turns: 250
Find the voltage induced in the secondary coil.
Since the secondary coil turns are half as many as those in the primary coil, the voltage induced will be half as much. Therefore, the induced voltage will be equal to 110 volts.
We refer to such transformers as “Step-Down Transformers”.